参考书目:Forsyth and Ponce, Computer Vision, Chapter 7
Filtering
用原始图像的像素点的组合构造新的图像。
Form a new image whose pixels are a combination of the original pixel values.
目的:
- 提取图像中有用的信息
- 特征(edges, corners, blobs)
- 修改,增强图像的某些属性
- Super-resolution; in-painting; de-noising.
举例:
-
Moving average
- 用相邻像素的平均值替换掉这个像素的值
- 平滑滤波,去掉sharp features.
-
Image segmentation
- 定义一个阈值,大于的取255,小于的取0
离散卷积(descret convolution)
符号 *
步骤:
- Fold h[k,l] about origin to form h[−k,−l], 模板翻转
- Shift the folded results by n,m to form h[n − k,m − l] 模板平移
- Multiply h[n − k,m − l] by f[k, l]
- Sum over all k,l
- Repeat for every n,m
original - blurred = detailed.
original + detailed = sharped.
也就是说
2倍的original - blurred = sharpped
假如图像是N1xM1,模板是N2xM2,卷积之后的结果是(N1+N2-1)x(M1+M2-1).
对原始图像超出了N1xM1的部分有多种处理方式:
- 补0(zero padding), matlab使用这种方式
假如矩阵是:
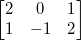
补0后:
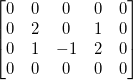
- 复制边界像素(edge replication)
- Mirror extension
- …
互相关(cross correlation)
符号 **
步骤:
互相关跟卷积的唯一不同就是模板不需要翻转。
性质:
- 交换律(commutative)
- 结合律(Associative)
- 分配率(Distributive)
- 移不变(shift-invariant)
卷积和互相关
A convolution is an integral that expresses the amount of overlap of one function as it is shifted over another function.
- convolution is a filtering operation
Correlation compares the similarity of two sets of data. Correlation computes a measure of similarity of two input signals as they are shifted by one another. The correlation result reaches a maximum at the time when the two signals match best.
- correlation is a measure of relatedness of two signals
Normalized Cross-Correlation
参考: http://scribblethink.org/Work/nvisionInterface/nip.html
在模板和图像的每个片段相乘之前,先把图像的这个片段的值做标乘(scaled)和平移(offset),使之均值为0,方差为1. 这个过程称之为归一化(Normalized).
如果图像片段的灰度值过高,跟模板的模式不匹配,这个过程可以提高精度。在matlab中采用normxcorr2完成这个过程。